Polarity
2020-06-20
What is polarity? What makes something polar?
A polar molecule is a molecule that has a positive and a negative end (or pole). For example, water (H2O) is a polar molecule.
▲
Check out The Penny Polarity Experiment for proof.
To understand why water is polar, you need to know three main ideas.
1. Atoms contain tiny negative particles called electrons. More electrons make something more negative. Electrons also help atoms stay together.
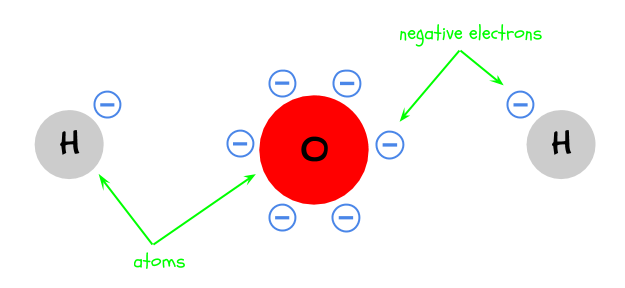
2. A water molecule is made of three atoms: two hydrogen and one oxygen. They are bonded together by sharing electrons.
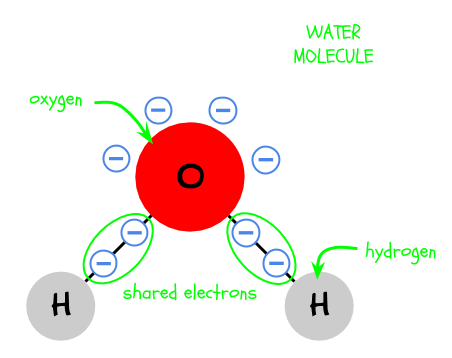
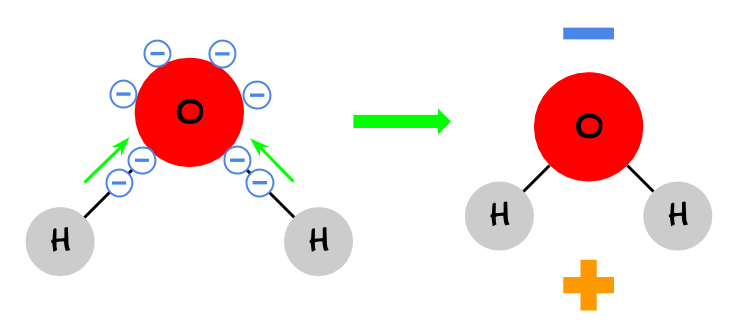
3. Oxygen “wants” electrons more than hydrogen. As a result, even though the oxygen and hydrogen are sharing electrons, the oxygen pulls the electrons more. Therefore, the side of the molecule with the oxygen is more negative.
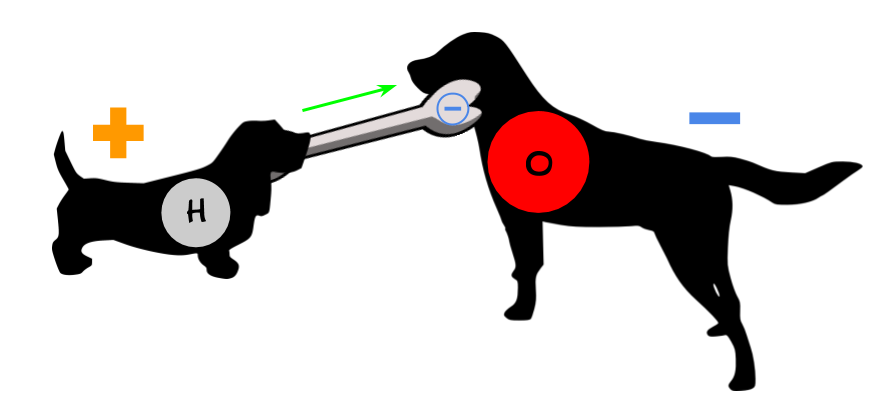
 You can think of electron sharing as two dogs (hydrogen and oxygen) playing tug-of-war with a bone (electrons). Because both dogs are holding onto the same bone, they are stuck together. Even though the bone moves back and forth between the two dogs, the stronger oxygen dog pulls on the bone more and gets it for more time.
You can think of electron sharing as two dogs (hydrogen and oxygen) playing tug-of-war with a bone (electrons). Because both dogs are holding onto the same bone, they are stuck together. Even though the bone moves back and forth between the two dogs, the stronger oxygen dog pulls on the bone more and gets it for more time.